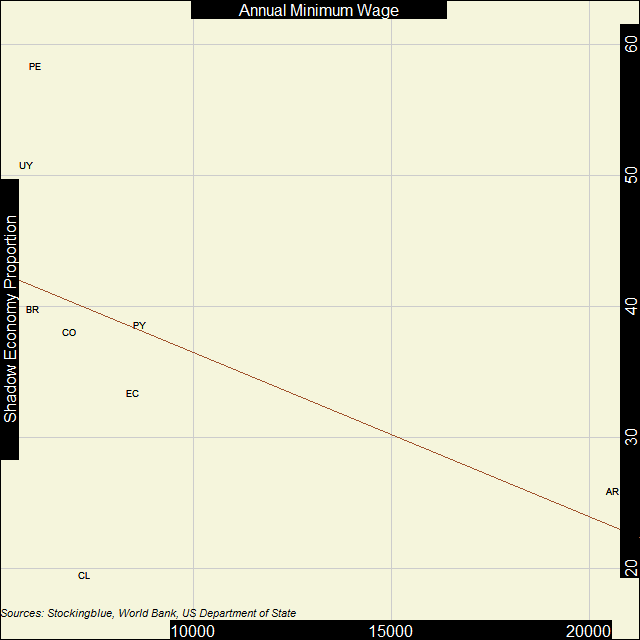
In South America, the inverse correlation between the strength of the shadow economy and the minimum wage is pretty weak. There is no real relationship between the strength of the shadow economy and minimum wage.
Findings
- The correlation coefficient between per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) and minimum wage in South America is -0.49.
- As the shadow economy increases in the continent, the minimum wage does not necessarily decrease.
- Argentina has the highest minimum wage, by far, but Chile has a smaller shadow economy.
- Peru, Uruguay, and Brazil all have similar minimum wages but the strength of their shadow economies varies considerably.
- Only Chile has a shadow economy that takes up less than one-fifth of its overall economy.
Caveats
- As always, correlation does not imply causation.
- Bolivia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela were missing data.
- Minimum wages sometimes vary by profession and other variables.
Details
There is a huge chasm between the Argentinian minimum wage and the rest of the South American countries' minimum wage. Yet Chile has a considerably smaller shadow economy and Ecuador is not far behind.
Just as in North America, there is no real correlation between the strength of a shadow economy and the minimum wage.
Country Codes
| Code | Country | Annual Minimum Wage | Shadow Economy (as Percentage of GDP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR | Argentina | 20,627 | 25.9 |
| BR | Brazil | 5,962 | 39.8 |
| CL | Chile | 7,253 | 19.5 |
| CO | Colombia | 6,853 | 38.1 |
| EC | Ecuador | 8,485 | 33.4 |
| PE | Peru | 6,014 | 58.4 |
| PY | Paraguay | 8,661 | 38.6 |
| UY | Uruguay | 5,766 | 50.8 |
Sources
US Department of State. 2017. "Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2016." Accessed September 2, 2017. https://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/humanrightsreport/index.htm#wrapper.
Schneider, Friedrich, Andreas Buehn, and Claudio E. Montenegro. 2010. "Shadow Economies All over the World: New Estimates for 162 Countries from 1999 to 2007." The World Bank Development Research Group.