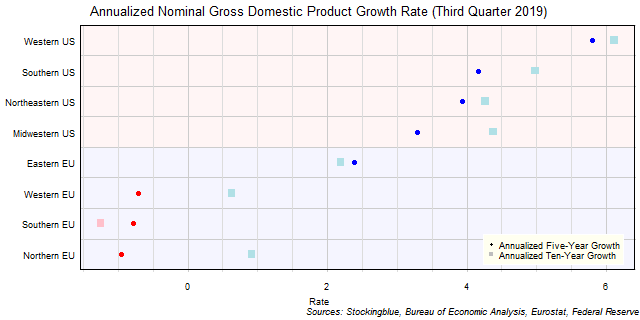
The chart above shows the annualized nominal gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate when priced in US dollars in each EU and US region over the past five years as of the third quarter of 2019 and the growth over the past ten years. All negative growth rates in the EU are attributed to currency rate fluctuations.
Findings
- The difference between the region with the largest annualized five-year growth rate, the Western US, and the region with the smallest, the Northern EU, is 6.75 percentage points.
- The difference between the region with the largest annualized ten-year growth rate, the Western US, and the region with the smallest, the Southern EU, is 7.36 percentage points.
- Two regions' economies (2 EU, 0 US) grew faster over the past five years than they did over the past ten years. Six regions' economies (2 EU, 4 US) saw their economies grow slower over the past five years than they did over the past ten years.
- All EU drops in growth rate are attributed to currency rate fluctuations.
Caveats
- Data is from the third quarters of 2009, 2014, and 2019.
- The data is seasonally adjusted in current dollars.
- Euros are converted to dollars at an average exchange rate of 1.11 for the third quarter of 2019, 1.32 for the third quarter of 2014, and 1.43 for the third quarter of 2009 according to historic rates listed at the Federal Reserve (see source link below).
- US data comes in an annualized format which the EU does not, thus EU data is annualized by multiplying the quarterly figure by four.
- US growth rates may differ from those provided by the Bureau of Economic Analysis as the BEA's growth rates are based on chained dollars in conjunction with the chain index or the quality index for real GDP. The growth rates listed here are based on nominal GDP.
- All figures are rounded to the nearest hundredth.
- The Eastern EU consists of Poland, Czech Republic, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Croatia, Slovenia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia.
- The Midwestern US consists of Illinois, Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Missouri, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota.
- The Northeastern US consists of New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Massachusetts, Maryland, Connecticut, New Hampshire, Delaware, Maine, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
- The Northern EU consists of Sweden, Denmark, and Finland.
- The Southern EU consists of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece, Cyprus, and Malta.
- The Southern US consists of Texas, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, Virginia, Tennessee, Louisiana, South Carolina, Alabama, Kentucky, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Mississippi, and West Virginia.
- The Western EU consists of Germany, United Kingdom, France, Netherlands, Belgium, Austria, Ireland, and Luxembourg.
- The Western US consists of California, Washington, Colorado, Arizona, Oregon, Utah, Nevada, New Mexico, Hawaii, Idaho, Alaska, Montana, and Wyoming.
Details
The Northern EU had the largest decrease over the past five years with an annualized drop of 0.96%. The Western US had the largest growth with an annualized gain of 5.80%.
Over the past ten years, the Southern EU had the largest decrease with a 1.25% drop in GDP while the Western US had the largest growth with a 6.11% rise in GDP.
The Northern EU saw the largest decrease in its growth rate between its annualized ten-year growth and its annualized five-year growth slowing its rate by 1.88 percentage points. The Southern EU had the largest increase in its growth rate between its annualized ten-year growth and its annualized five-year growth raising its rate by 0.46 percentage points.
The Northern EU went from having a higher growth rate than each of the Southern and Western EU over the past ten years to a lower one over the past five years. The Midwestern US also went from having a higher growth rate than the Northeastern US over the past ten years to a lower one over the past five. The Northern EU had the smallest range in annualized five-year growth rates with a low of -3.75% in Sweden to a high of -0.20% in Finland. Conversely, the Western EU had the greatest range in annualized five-year growth rates with a low of -2.43% in the United Kingdom to a high of 9.97% in Ireland. Over the past ten years, the Northern EU had the smallest range in growth rates with a low of 0.44% in Finland to a high of 1.50 in Sweden. The Southern EU on the other hand, had the greatest range of rates on a ten-year basis with a low of -3.85% in Greece to a high of 6.80% in Malta.
Sources
Eurostat. 2020. "GDP and Main Components." Accessed March 10, 2020. https://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?query=BOOKMARK_DS-406779_QID_-12E83AF1_UID_-3F171EB0&layout=TIME,C,X,0;GEO,L,Y,0;UNIT,L,Z,0;S_ADJ,L,Z,1;NA_ITEM,L,Z,2;INDICATORS,C,Z,3;&zSelection=DS-406779UNIT,CP_MEUR;DS-406779INDICATORS,OBS_FLAG;DS-406779S_ADJ,SCA;DS-406779NA_ITEM,B1GQ;&rankName1=UNIT_1_2_-1_2&rankName2=INDICATORS_1_2_-1_2&rankName3=NA-ITEM_1_2_-1_2&rankName4=S-ADJ_1_2_-1_2&rankName5=TIME_1_0_0_0&rankName6=GEO_1_2_0_1&sortC=ASC_-1_FIRST&rStp=&cStp=&rDCh=&cDCh=&rDM=true&cDM=true&footnes=false&empty=false&wai=false&time_mode=NONE&time_most_recent=false&lang=EN&cfo=%23%23%23%2C%23%23%23.%23%23%23.
Federal Reserve. 2020. "Foreign Exchange Rates." Accessed March 11, 2020. https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g5/.
US Bureau of Economic Analysis. 2020. "GDP by State." Accessed March 9, 2020. https://www.bea.gov/data/gdp/gdp-state.