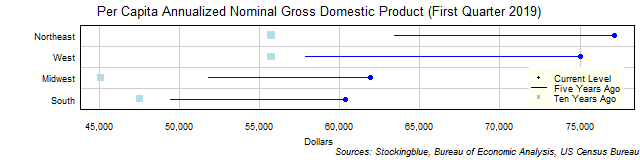
The chart above shows the per capita annualized nominal gross domestic product (GDP) in each US region as of the first quarter of 2019 in dollars, the change from five years ago, and the per capita GDP ten years prior. Every single region's economy grew both over the past five and past ten years.
Findings
- The difference between the region with the largest per capita GDP, the Northeast, and the region with the smallest, the South, is $16,777.61 (up from $13,953.36 five years ago and up from $10,646.48 ten years ago). The Northeast and the South had the largest and smallest per capita GDP respectively five years ago while the Northeast and the Midwest had the largest and smallest per capita GDP respectively ten years ago.
- The Northeast has 1.28 times the per capita GDP that the South does. The ratio of largest per capita GDP to smallest per capita GDP stayed steady at 1.28 from five years ago and up from 1.24 ten years ago.
- All four regions saw their per capita GDP rise in current dollars over the past five years.
- All four regions saw their per capita GDP rise in current dollars over the past ten years.
Caveats
- GDP data is from the first quarters of 2009, 2014, and 2019.
- Census data is from 2000 and 2010.
- The data is seasonally adjusted in current dollars.
- Growth rates may differ from those provided by the Bureau of Economic Analysis as the BEA's growth rates are based on chained dollars in conjunction with the chain index or the quality index for real GDP.
- All figures are rounded to the nearest hundredth.
- The Northeastern US consists of New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Massachusetts, Maryland, Connecticut, New Hampshire, Delaware, Maine, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
- The Western US consists of California, Washington, Colorado, Arizona, Oregon, Utah, Nevada, New Mexico, Hawaii, Idaho, Alaska, Montana, and Wyoming.
- The Midwestern US consists of Illinois, Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Missouri, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota.
- The Southern US consists of Texas, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, Virginia, Tennessee, Louisiana, South Carolina, Alabama, Kentucky, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Mississippi, and West Virginia.
Details
In absolute terms, the Midwest saw the smallest increase over the past five years with a growth of $10,139.24. The West had the largest growth with a gain of $17,158.78. Over the past ten years, the South had the smallest increase with a gain of $12,849.71 while the Northeast had the greatest increase with a gain of $21,397.31.
In relative terms, the Midwest had the smallest increase over the past five years with a 19.58% rise in per capita GDP while the West had the greatest increase with a 29.66% rise in per capita GDP. Over the past ten years, the South had the smallest growth with a 27.04% rise in per capita GDP while the Northeast had the largest growth with a 38.38% rise in per capita GDP.
There were zero regions with a per capita GDP of over $60,000 ten years ago, one region five years ago, and four regions now. On the flip side, there were two regions with a per capita GDP of less than $50,000 ten years ago, one region five years ago, and zero regions now.
The Midwest and the South each have a lower per capita GDP now than the Northeast did five years ago. Every region has a higher per capita GDP now than any other region had ten years ago.
Sources
US Bureau of Economic Analysis. 2019. "GDP by State." Accessed August 18, 2019. https://www.bea.gov/data/gdp/gdp-state.
United States Census Bureau. September 2012. "United States Summary: 2010: Population and Housing Unit Counts." Accessed January 23, 2018. https://www.census.gov/prod/cen2010/cph-2-1.pdf.